Main menu
You are here
Model entry
| Search | Simulistics | Model catalogue | Listed by keyword | Listed by ID | Listed by title | Listed by date added |
One-compartment mixing process
Model : Muller1-1a
Simile version : 4.0
Date added : 2004-10-27
Keywords :
Mixing, solution ;
Basic System Dynamics ;
Description
This model illustrates the use of System Dynamics to model a simple mixing process. It is model Mod1-1a of Muller (2000) implemented here in Simile.
The system comprises a flask with an inlet and an outlet containing a volume of salt solution of one concentration. Solution is pumped in and out at the same rate. The in-flow of salt solution is of another concentration. Assuming the contents of the flask is well mixed, what is the concentration of the solution in the outlet over time.
Simile integrates using numerical methods, either Euler or 4th-order Runge-Kutta. The second is more accurate for truly continuous variables but fails if discontinuities (step changes) are present. Because of this the Euler method is used by default in Simile as many models include step changes. However, the system described here is continuous and the 4th-order Runge-Kutta performs better. This problem can be solved analytically and the equation for Wsalt_analytical does so allowing the numerical methods used by Simile to be evaluated. Have a play changing the integration method and time step. The results section shows a couple of runs of the model with different integration method setting.
Files
Model fileClick on the icon to download the model file. (You will need Simile to examine and run the model. A free evaluation version is available from the products page.) Some browsers may attempt to display the model file, rather than open it in Simile; in this case, use the browser back button to return to this page, and use the context menu (invoked by right-clicking on the link) to save the target file to disk. |
|
|
|
|
Diagram
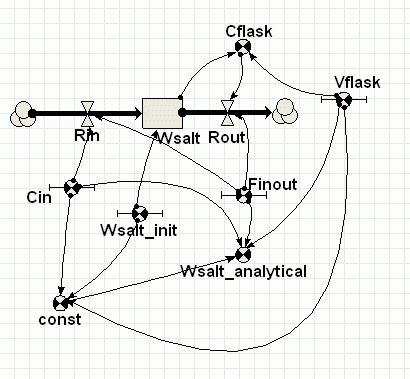
Equations
Compartment Wsalt : g Initial value = Wsalt_init Rate of change = + Rin - Rout Flow Rin Rin = Cin*Fin Where: Fin=Finout Flow Rout Rout = Cflask*Finout Variable Cflask Cflask = Wsalt/Vflask Comments: g/l Variable Wsalt_analytical Wsalt_analytical = -(Vflask*(exp(-(Finout*time(0)+const)/Vflask)-Cin)) Variable const const = -(log(Cin-Wsalt_init/Vflask)*Vflask)
Results
|Integration method: Euler
Time step : 0.1

Integration method: 4th-order Runge-Kutta
Time step : 0.5
N.B. The traces for the analytical and the numeric, 4th-order Runge-Kutta, intergration overlap.

References
Muller, C. 2000 Modelling soil-biosphere interactions. CABI Publishing Oxford and New York pp 354
Copyright 2003-2024 Simulistics Ltd
